Day 37
Math 216: Statistical Thinking
Bastola
Key Assumptions for Linear Regression
Key Question: What conditions must be met for our regression results to be valid?
Simple Linear Regression Model:
- \(y = \beta_0 + \beta_1 x + \varepsilon\)
Four Critical Assumptions:
- Mean of Errors (\(\varepsilon\)): The mean of the probability distribution of \(\varepsilon\) is 0, aligning the expected value of \(y\) with \(\beta_0 + \beta_1 x\) for any \(x\)
- Constant Variance: The variance of \(\varepsilon\) is constant across all values of \(x\), denoted as \(\sigma^2\)
- Normal Distribution of Errors: \(\varepsilon\) follows a normal distribution
- Independence of Errors: The errors associated with different \(y\) values are independent
Constant Variance
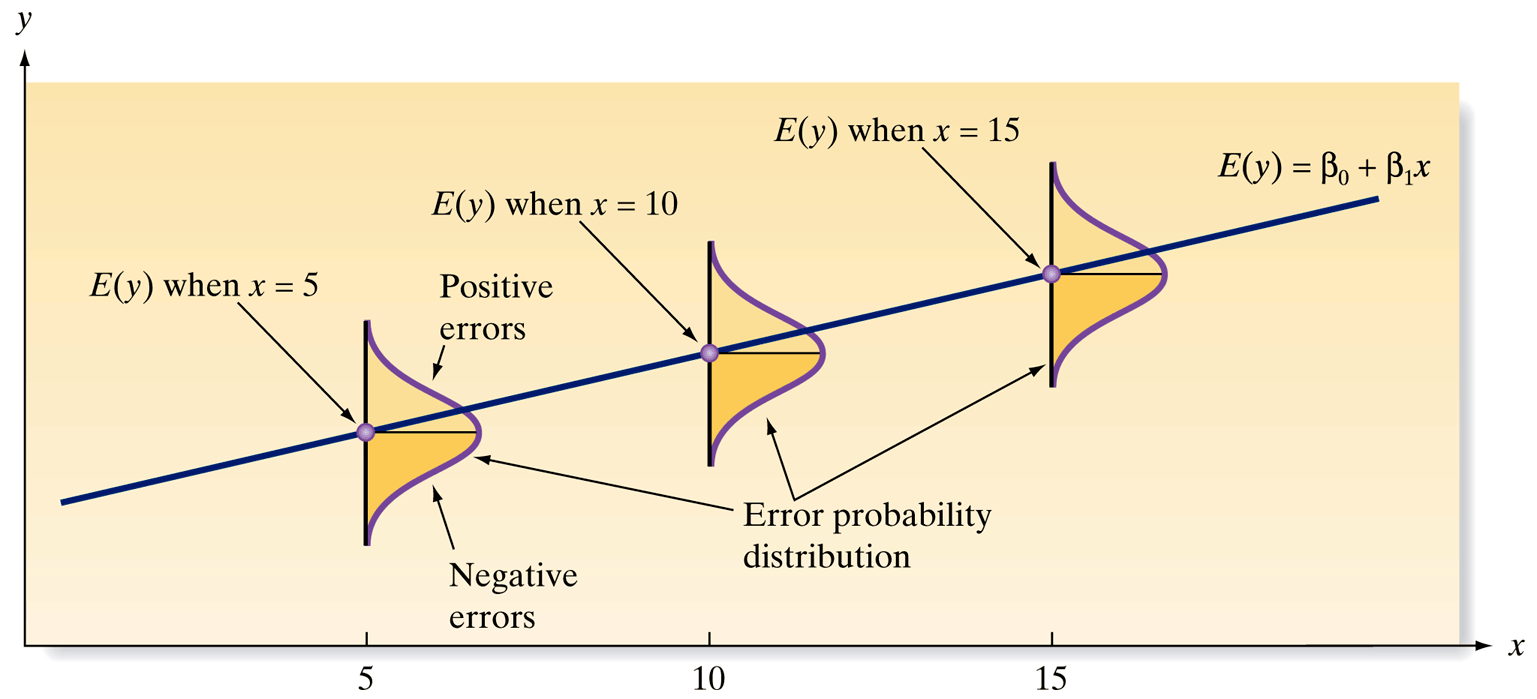
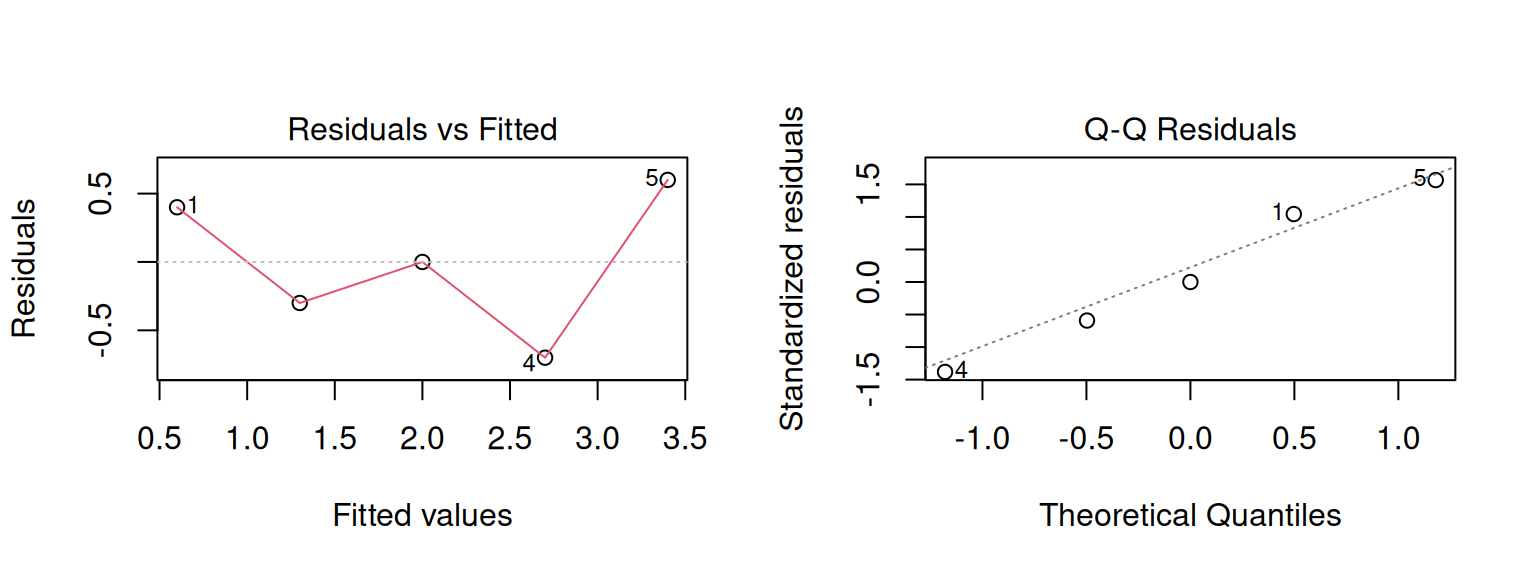
How do we check regression assumptions?
Interpreting Diagnostic Plots:
- Residuals vs Fitted: Check constant variance (no patterns)
- Normal Q-Q: Check normality (points follow straight line)
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x)
Residuals:
1 2 3 4 5
4.000e-01 -3.000e-01 -5.551e-17 -7.000e-01 6.000e-01
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -0.1000 0.6351 -0.157 0.8849
x 0.7000 0.1915 3.656 0.0354 *
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
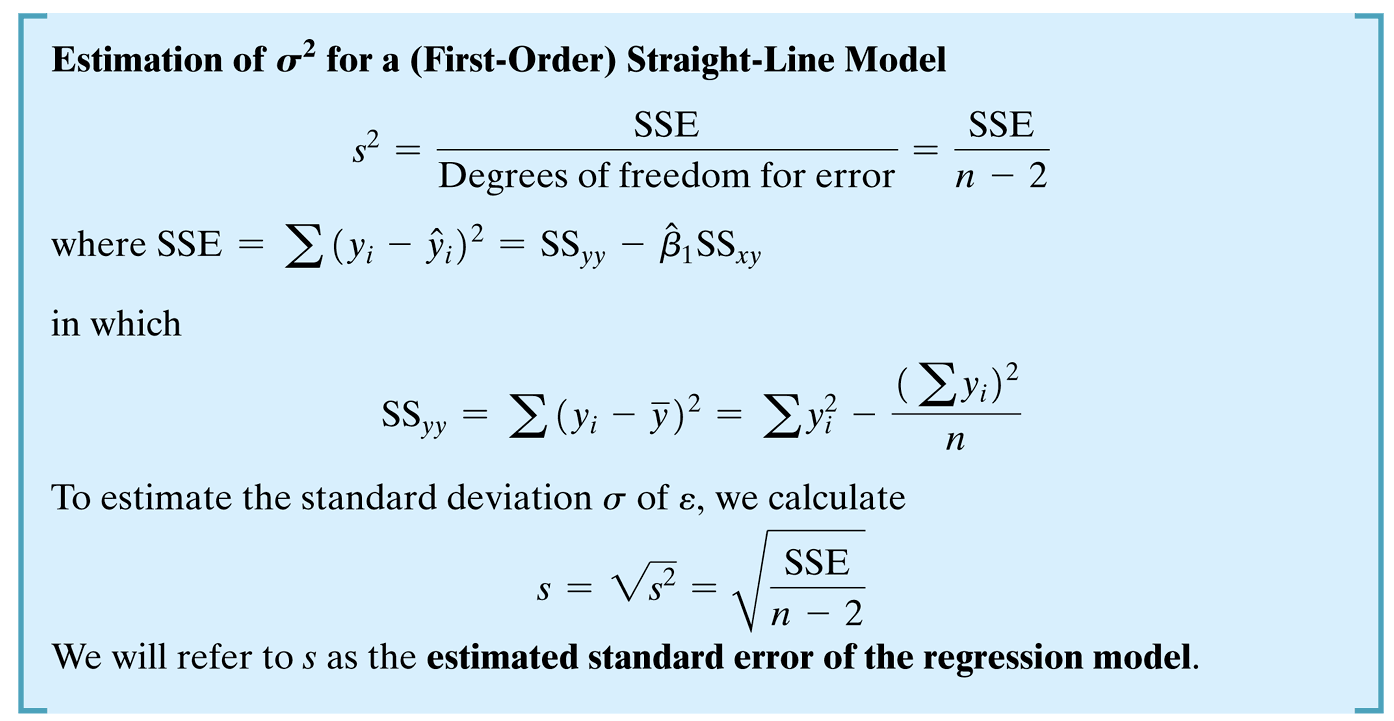
Residual standard error: 0.6055 on 3 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.8167, Adjusted R-squared: 0.7556
F-statistic: 13.36 on 1 and 3 DF, p-value: 0.03535Making Inferences About the Slope \(\beta_1\)
Key Question: Is the relationship we found statistically significant, or just random chance?
- Objective: Assess the significance of the slope \(\beta_1\) to understand if \(x\) truly helps predict \(y\)
- Statistical Test:
- Null Hypothesis (\(H_0\)): \(\beta_1 = 0\) (No relationship - changes in \(x\) don’t affect \(y\))
- Alternative Hypothesis (\(H_a\)): \(\beta_1 \neq 0\) (Significant relationship - \(x\) does affect \(y\))
- Using R for Hypothesis Testing:
- Perform t-tests to decide whether to reject \(H_0\)
- A significant \(p\)-value (\(< \alpha\)) indicates a meaningful contribution of \(x\) to predicting \(y\)
Real-World Insight: This test tells us if our predictor variable is actually useful, or if we’re just seeing patterns in random noise!
Practical Steps Using R
Key Question: How do we actually test for slope significance in R?
- Conducting the Test:
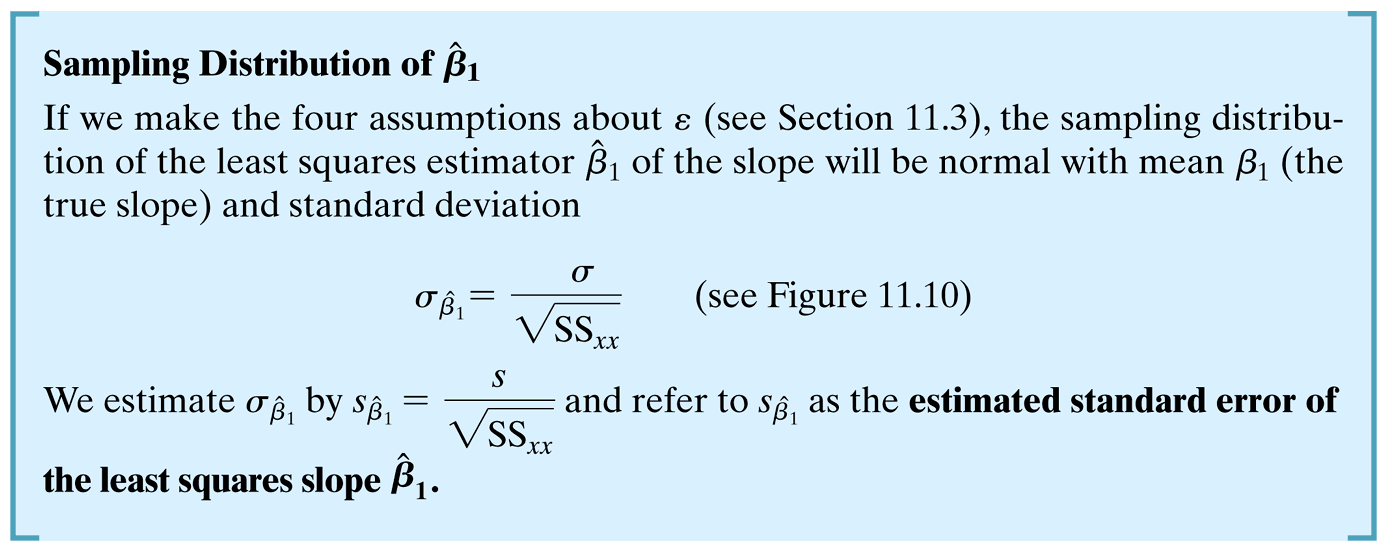
- Estimate \(\hat{\beta}_0\) and \(\hat{\beta}_1\) using the least squares method
- Compute the standard error and perform a t-test to check the significance of \(\hat{\beta}_1\)
- Interpret the results: A significant test suggests that changes in \(x\) systematically relate to changes in \(y\)
Real-World Application: This process transforms our regression output into actionable insights about variable relationships!
Hypothesis Testing
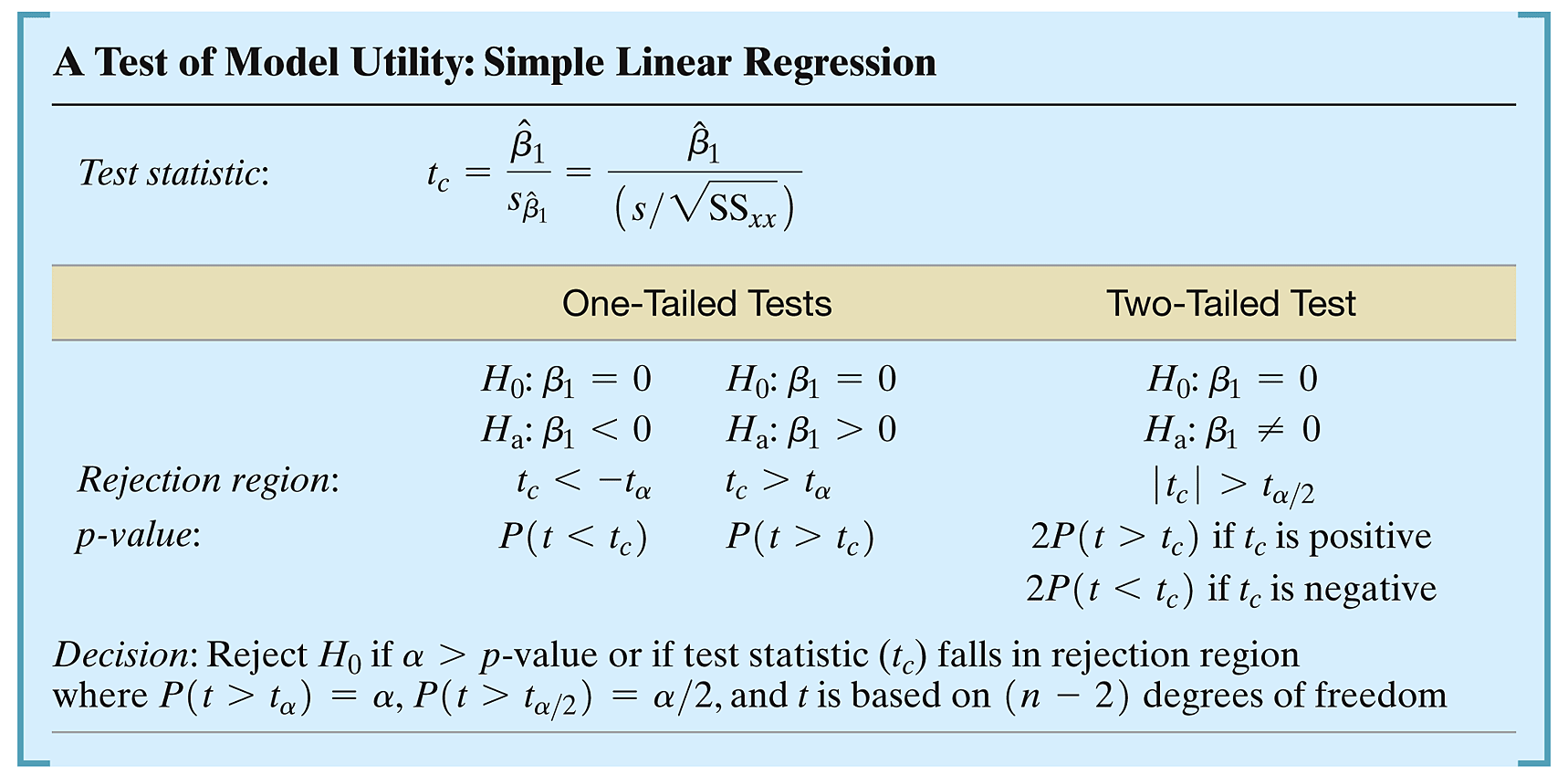
How can we make a decision of this hypothesis test using R?
|
Regression Hypothesis Testing Framework
%%{init: {"theme": "base", "themeVariables": {"fontSize": "30px", "fontFamily": "Arial", "lineColor": "#333"}}}%%
flowchart LR
%% --- Styling Definitions ---
classDef start fill:#FFFACD,stroke:#FF8C00,stroke-width:2px,color:#000
classDef decision fill:#E6F3FF,stroke:#1E88E5,stroke-width:2px,color:#000
classDef action fill:#E8F5E9,stroke:#43A047,stroke-width:2px,color:#000
classDef endStyle fill:#FFEBEE,stroke:#E53935,stroke-width:2px,color:#000
%% --- Nodes ---
%% Using <br/> to balance width and height
A([Start:<br/>Regression Model]):::start
B{"State Hypotheses<br/>H₀: β₁ = 0<br/>vs<br/>Hₐ: β₁ ≠ 0"}:::decision
C{"Calculate Statistic<br/>t = b₁ / SE(b₁)"}:::decision
D{"Compute p-value<br/>(t-dist)"}:::decision
E{"Compare p-value<br/>to α = 0.05"}:::decision
F["Reject H₀<br/>Significant"]:::action
G["Fail to Reject H₀<br/>No Evidence"]:::action
H["Interpret<br/>Results"]:::endStyle
%% --- Connections ---
A --> B
B --> C
C --> D
D --> E
E -->|p < .05| F
E -->|p ≥ .05| G
F --> H
G --> H
%% --- Visual Polish ---
linkStyle default stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px;
Confidence Intervals
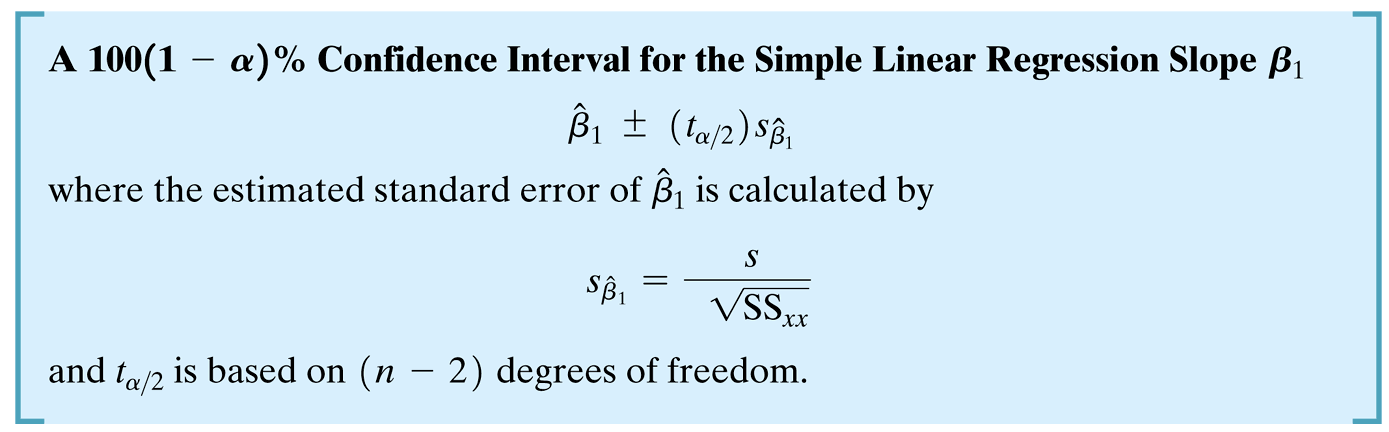
Confidence Intervals in R
2.5 % 97.5 %
(Intercept) -2.12112485 1.921125
x 0.09060793 1.309392